Cementing is an important task in the drilling process. In drilling operations, there must be at least two cementing (production wells) and up to 4 to 5 cementing (deep exploration wells). The top cementing is the surface casing cementing, which plays the role of "mud passage, oil and gas portal". Before the next drilling, the surface casing should be equipped with a blowout preventer to prevent blowout. A mud pipe is installed on the blowout preventer, which is a passage for the drilling fluid to return to the mud pool. In the drilling process, technical casing cementing is often required, which plays the role of “consolidating the rear and safely exploring the road”. Like the road tunnels and the roadways in the coal mines, the wells will encounter well collapses, high pressures and unstable formations during the drilling process. At the same time, they will also have a retreat in the case of distress in the forward "pathway" and play a "rescue". effect.
Cementing is divided into three steps: casing, cementing, wellhead installation and casing pressure test.

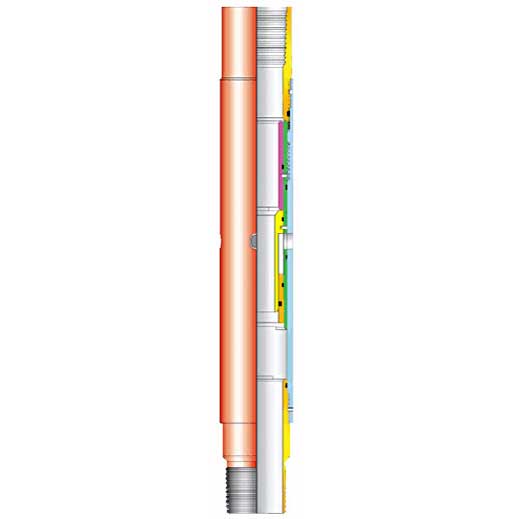
The casings are available in different sizes and steel grades. Surface cementing usually uses 20~13 3/8 inch casings, most of which are steel grade "J" grade casings. Technical casings typically use 13 3/8 to 7 inch casings with a higher steel grade. Oil casing casing cementing usually uses 7 to 5 inch casing, and the steel grade strength is the same as that of the technical casing. The strength of the casing is designed according to the application, formation prediction pressure and casing penetration depth, and the wall thickness, steel grade and thread type of the casing are determined.
The casing is different from the drill pipe. It is a one-time pipe that is not required to be thickened. The length is not strictly regulated. In order to ensure the cementing quality and smoothly enter the casing, the structural design of the casing string is to be carried out.

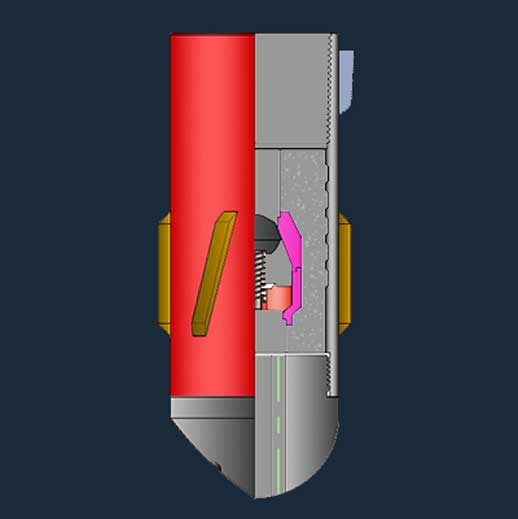
It is the key process after the casing enters the well. Its function is to seal the annular space of the casing and the well wall to seal the oil and gas water layer and make the casing become the passage of oil and gas into the well.
Oil well cement is an important material for sealing the casing and the annular space of the well wall. Because the well is deep and shallow, the underground has atmospheric pressure and high temperature and high temperature, and the formation also contains various chemical substances, so the oil well cement is required to have a wide adaptability. At present, there are 9 grades and three types of oil well cement used in China. Different grades and types of cement are suitable for different downhole conditions. Therefore, selecting cement according to the depth and temperature of the well is the primary task of cementing operations.
The limited cement grade does not meet the performance requirements of grouting. The G-grade and H-grade cements used today are often modified with additives to adjust their performance. They are the most commonly used cements. Additives can be divided into seven categories: adjusting the density agent, adjusting the setting time additive, controlling the loss additive, reducing the water loss agent, controlling the viscosity agent, and special additives for abnormal conditions. One level of cement may use one or more additives.
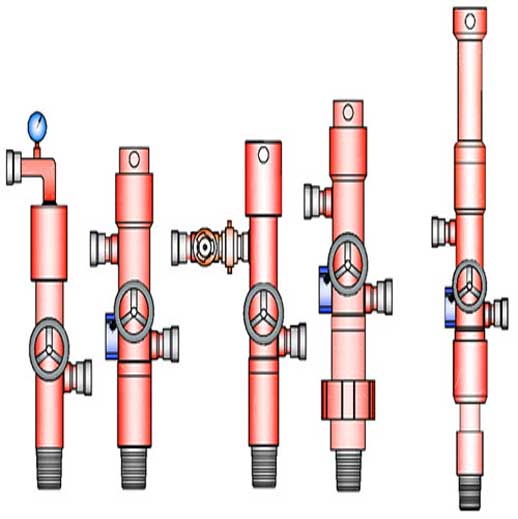
Immediately after the casing is completed, the circulating pipeline and the cementing pipeline are connected to prepare for cementing. First of all, it is necessary to open the pump to circulate the drilling fluid. Because the gap between the casing and the well wall is small, the high return speed is used to impact the mud cake on the well wall, and the performance of the drilling fluid is adjusted until the circulating pump pressure is stable. During this period, the start of the cementing pump, ash, water supply, mixing, and suctioning should be ready, as shown in Figure 6-8.
Before the cement slurry is injected into the casing, a certain amount of pre-fluid is pumped to isolate the drilling fluid and the cement slurry to avoid mixing. Moreover, after the separator returns to the casing, it also serves to clean the annular space.
The displacement rate of the cement slurry depends on the conditions in the well. If there is no special situation, high-speed turbulence displacement should be adopted. However, in the case of low formation fracture pressure, only low speed replacement can be used.
After the casing is cemented, the wellhead is installed during the solidification of the cement. The top end of the surface casing is to be the casing of the casing head. The top end of each layer of casing is hung in the casing head. The casing head is mainly used to support the weight of the technical casing and the oil casing, which is especially important for the cementing cement not returning to the ground. The casing head is also used to seal the annular space between the casings to prevent pressure build-up. The casing head is also a transitional connection between the blowout preventer and the tubing head. There are also two side ports on the casing head for use on the land to replenish cement and monitor well conditions. Note the operation of balance liquid.
Casing pressure testing is an important part of checking cementing quality. After installing the casing head and connecting the blowout preventer and the blowout preventer line, the pressure resistance check of the casing head seal and the seal pressure test connected with the blowout preventer are required. After testing the cement plug in the casing, the pressure test of the casing string should be carried out. After drilling through the casing shoes for 2~3 meters (technical casing), the ground fracture test should be carried out. The production well should be tested for the quality of the cement ring, and the sound wave should be used to detect the cementation of the cement ring and the casing and the borehole wall. After all the indicators of cementing quality are qualified, the next operating procedure can be entered.
0531-69959201
lqg18653457231
+86-18653457231
No 12111,Jingshi Road, Lixia District, Jinan City, Shandong Province. P.R. China
 English
English  日本語
日本語  français
français  Español
Español  русский
русский  português
português  العربية
العربية  tiếng việt
tiếng việt  ไทย
ไทย  Polska
Polska  română
română